Continuum Mechanics and Computational Geomechanics
Qi ZHANG 張琦
Assistant Professor 助理教授 博士生導師
Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering 土木與環境工程系
University of Macau 澳門大學
Official webpage: https://www.fst.um.edu.mo/people/qzhang/; https://www.fst.um.edu.mo/cee/acadstaff/; https://www.fst.um.edu.mo/people/academic-staff/
Publication data: see this Word file
Contact
Feel free to stop by my office at E11-3009 if you are interested in my research. For potential Ph.D. students or 碩士想進組的澳大學生, please make sure you have obtained a good grade in calculus, linear algebra, and probability, for example, you should know at least 70% of the mathematics here. The university general guidelines for applying Ph.D. programs are posted here. The current university scholarship (for new incoming Ph.D. students) type is called UM PhD Teaching Research Assistant. Previous experience in numerical modeling is greatly appreciated.
The University-Funded Postdoctoral Fellow information could be find here.
請注意:國家留學基金委不支持從內地前往香港和澳門地區進行聯合培養(博士和博後都不行)!
Brief biography
Qi Zhang received his M.Sc. and Ph.D. in Civil and Environmental Engineering (area of Mechanics and Computation) from Stanford University under the supervision of Professor Ronaldo I. Borja. Before joining the University of Macau, he worked as a Research Assistant Professor in collaboration with Professor Zhen-Yu Yin.
Group member (by last name)
Xiaoran SHENG (B.Eng. from Hohai University, M.Sc. from CityU)
Yuquan WANG (B.Eng. from Hohai University, M.Sc. from SYSU)
Daokun XIE (M.Sc. student, B.Eng. from China University of Mining and Technology-Beijing)
Haoliang ZHANG (B.Eng. from Guangxi University, M.Sc. from Wuhan University)
Zilong ZHANG (Ph.D. from 3SR Laboratory, University of Grenoble Alpes)
Zikang HUANG (M.Sc. graduate from PolyU)
Ziqi TANG (Currently a Ph.D. candidate at PolyU)
Zaiyong WANG (Currently a Postdoc Fellow at Shenzhen University)
Xianhan WU (Currently a Ph.D. candidate at SUSTech and PolyU)
Academic outreach/service
- 2025年粵港澳大灣區“未之星”訓練營(華南理工大學、香港大學、澳門大學) [WeChat post]
- Special issue editor of several SCI journals
- Reviewer for many prestigious geomechanics journals such as Géotechnique, Acta Geotechnica, and RMRE
- Youth Editorial Board of AGER journal (2021, 2022)
- Youth Editorial Board of Rock Mechanics Letters (2025)
Academic awards
Research interests
My research interests span several areas:
- Computational Poromechanics. I am interested in understanding and controlling the fundamental mechanical processes that determine the formation and recovery of earth resources from sedimentary rocks to achieve energy and environmental sustainability.
- Data-driven approach for engineering. Statistical learning methods are used to help identify potential hazards in the coal mining and tunneling process such as water inrush and overburden failure.
- Physics-Informed Neural Network for geomaterials. One of the promising research direction that I am trying to work on is FEM/FVM Discretization-Guided Machine Learning in complex geomaterials or nonlinear continuum mechanics.
Research demo
I. Double porosity media 什麼是雙重孔隙介質?
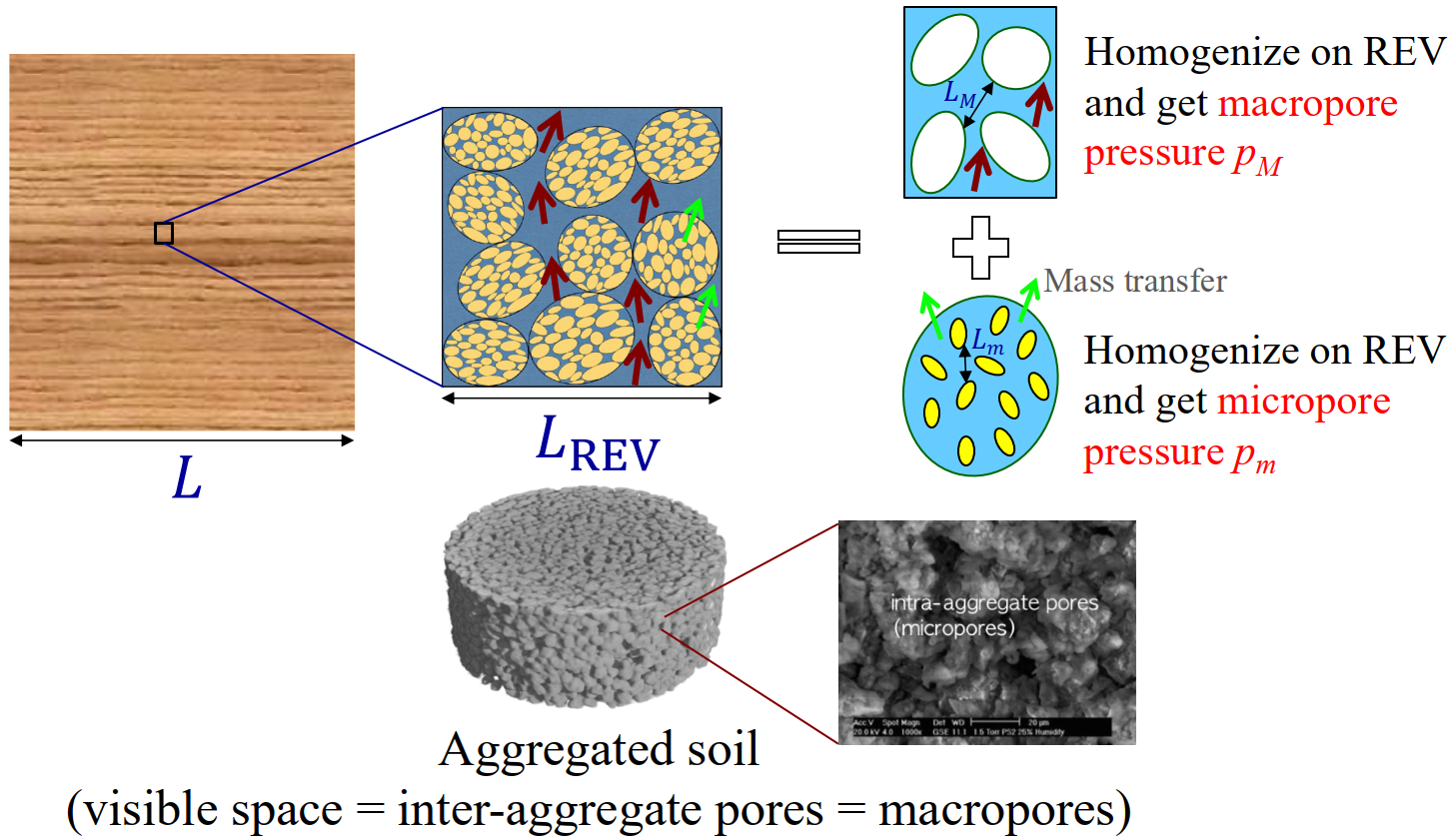
實際的雙重孔隙土壤樣品(附有掃描電鏡圖像)以及雙重孔隙介質的示意圖,其中包含多個不同的長度尺度,它們之間滿足 LM, Lm ≪ LREV ≪ L. 在每個宏觀物質點上,同時存在兩個壓力場 pM 和 pm
II. Double porosity media poroelastic coefficients derivation 雙重孔隙介質多孔彈性常數推導(特別針對各向異性材料)
- Mixture theory 混合物理論法
- Phenomenological approach 唯象法

III. Double porosity media hydromechanical coupling (time scale difference) 雙重孔隙介質流固耦合(時間尺度差異)
- Transversely isotropic equivalent fracture permeability 裂縫滲流各向異性
- Low-velocity non-Darcy flow of rock matrix 基岩低速非達西滲流
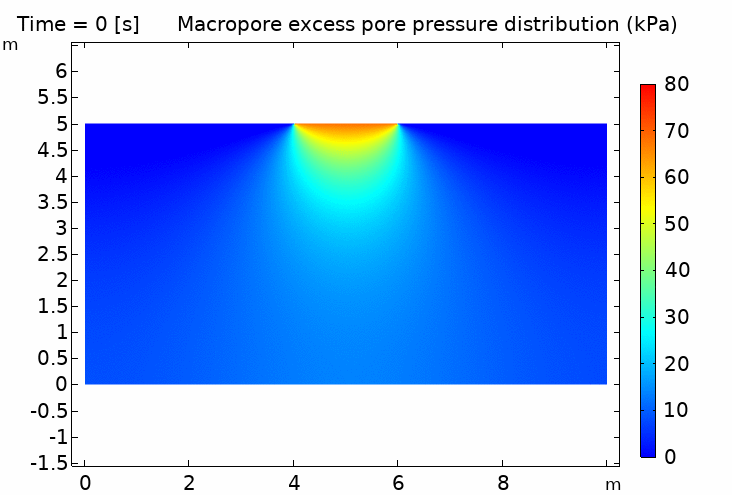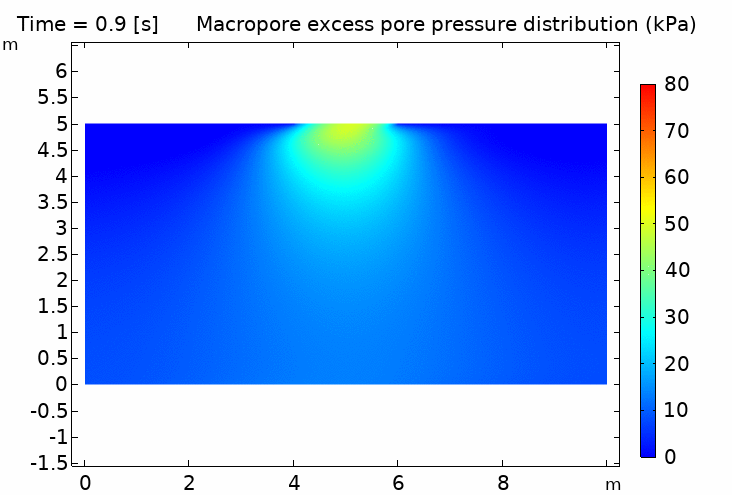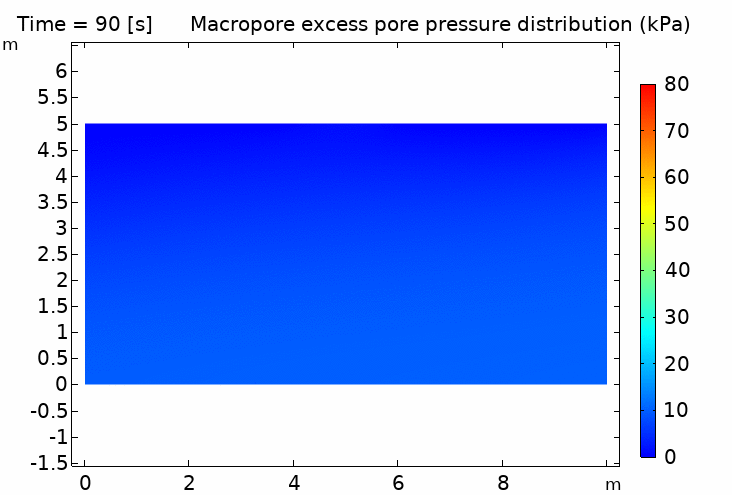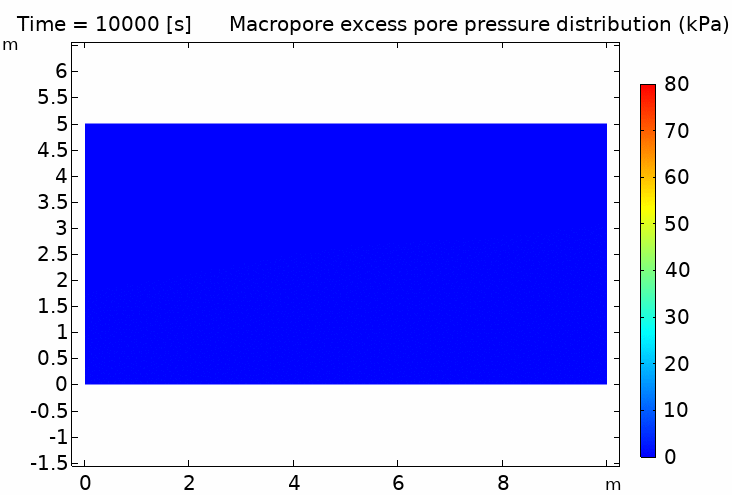
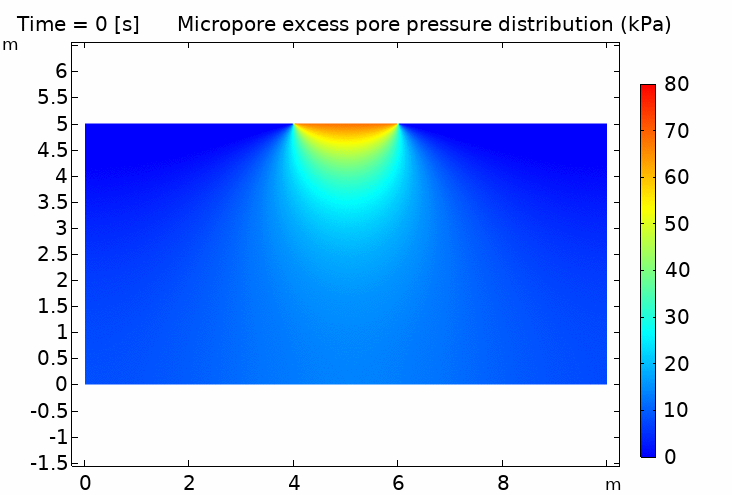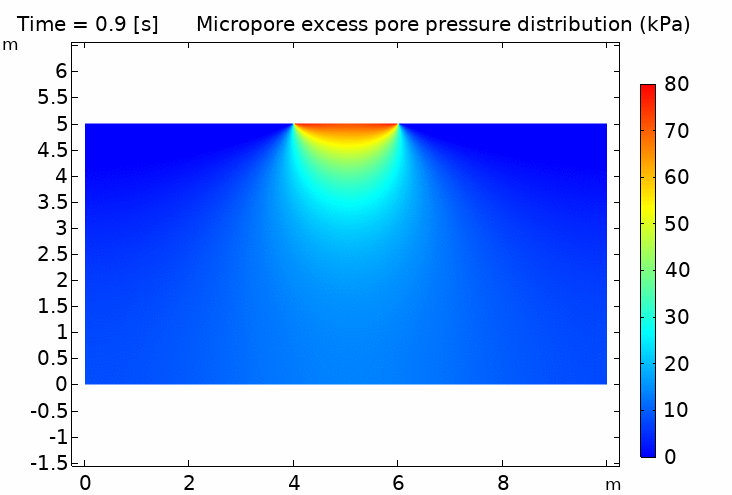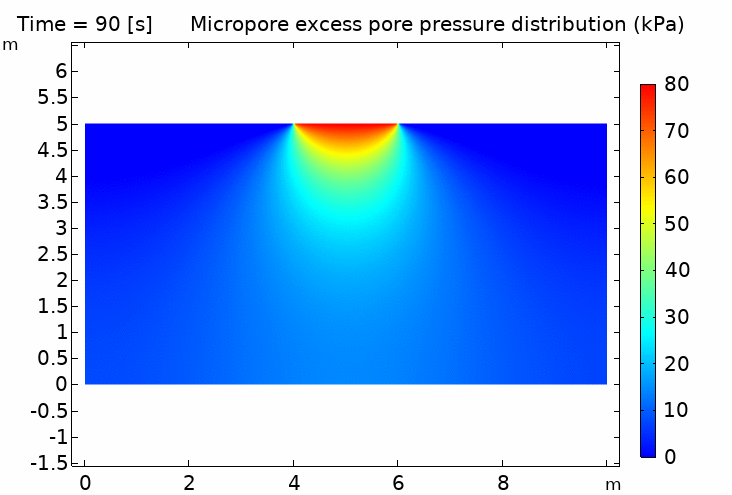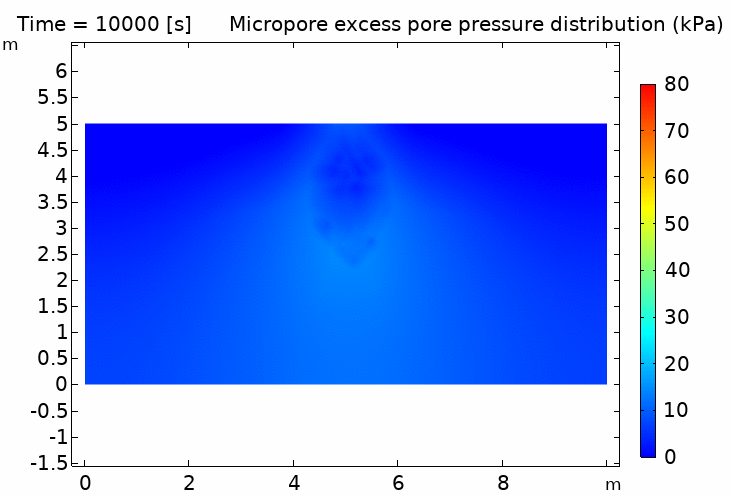
IV. Thermo-hydro-mechanical coupling in porous media (pipeline penetration simulation) 多孔介質熱流固耦合 (管道貫入模擬) 100℃ pipeline / 5℃ soil
- A video (zoomed-in area surrounding the pipeline) showing how incremental equivalent plastic strain (Incremental PEEQ) changes throughout the entire penetration process (frictionless/smooth contact and Mohr-Coulomb plasticity model are adopted here)
- A video showing how excess pore water pressure (Excess PWP) changes throughout the entire penetration process (frictionless/smooth contact and Mohr-Coulomb plasticity model are adopted here)
Open source code repository
FEM and PDE tool for fractured solid: This repository provides a MATLAB-based framework for simulating gas flow and solid deformation in unconventional anisotropic solid. The code is intended for a variety of scenarios and supports multiple fluid types, finite element formulations, and constitutive models.
Point simulation: This repository summarized several elastoplastic constitutive models, which are given in the time-integrated fully implicit form. Some classical stresss point simulations are also provided. Following constitutive models are considered: (1) ideal Drucker-Prager plasticity; (2) Modified Cam-Clay in which the isotropic elastic matrix is updated explicitly; (3) anisotropic MCC model for transversely isotropic rocks such as shale; (4) saturation-dependent anisotropic elasticity.
Photos for fun