Research Thrusts
Machine learning in geotechnical engineering
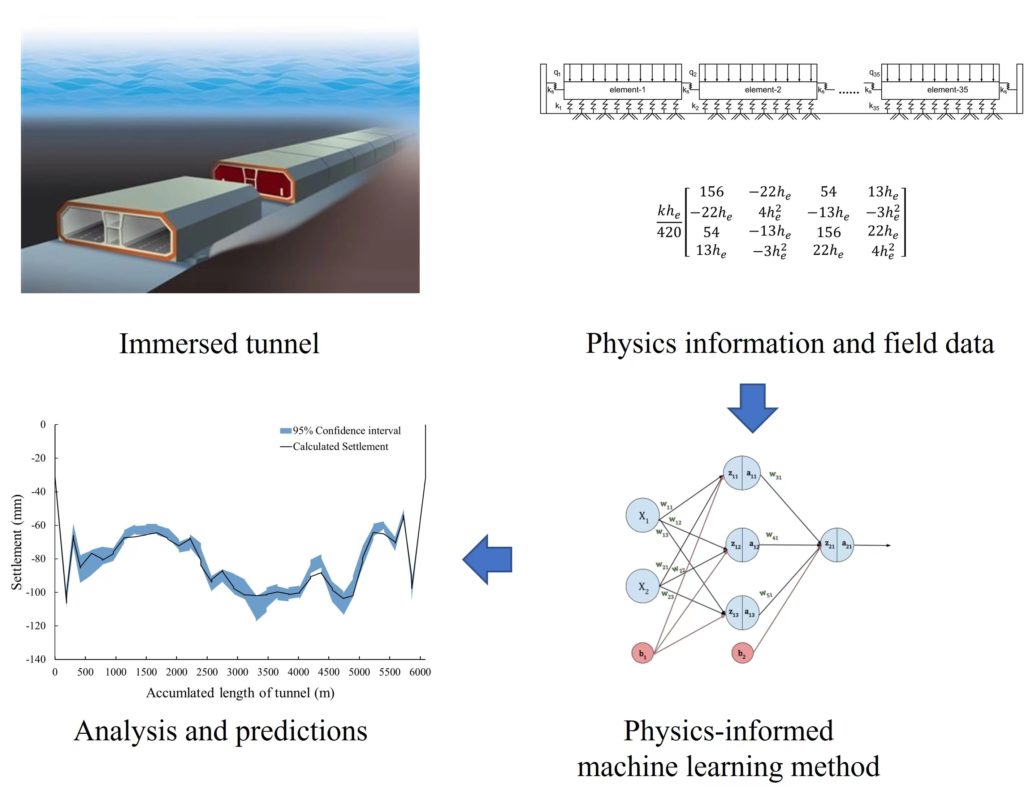
Physics-informed machine learning for settlement analysis for the immersed tunnel
In the service period of an immersed tunnel, large differential settlement may lead to some serious safety hazards. Generally, the settlement prediction faces several uncertainties, including the complex stratigraphic distribution problem, errors of measurement, etc. To against those difficulties, a physics-informed machine learning method was used to analyze the foundation modulus distribution of a tunnel through a multi-beam model, to predict its settlement.
Member: He Shu-yu
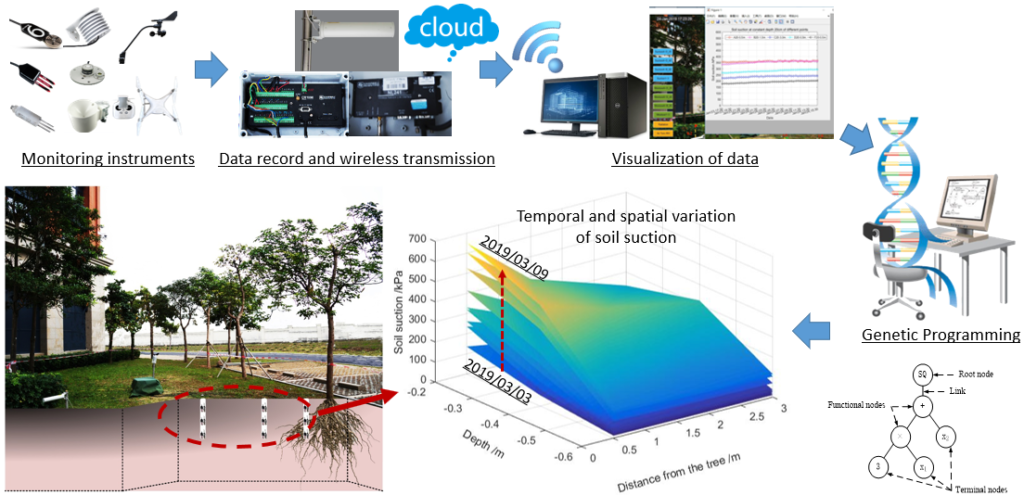
Physics-guided Machine Learning
Accurate calculation or prediction of key parameters’ variation in a complicated system is significant. A physics-guided genetic programming (PGGP) method is proposed to better calculation or prediction of field-monitored key parameters’ variation under the influence of multiple factors. The computational model can be established to explicitly depict the relationships among different parameters. The error analysis and uncertainty analysis are employed to evaluate the behavior of the obtained model, and the global sensitivity analysis and parametric study are performed to further reveal the parameter’s importance and interaction mechanism between influential parameters.
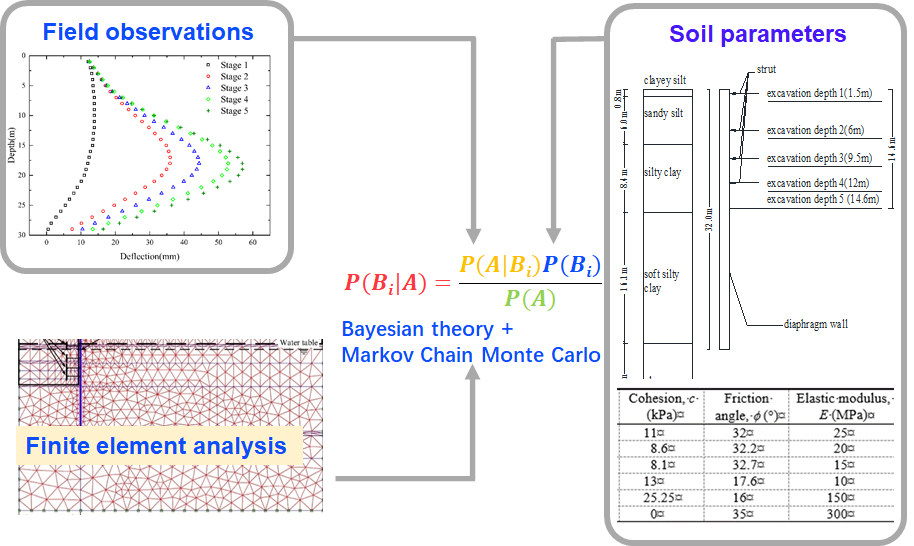
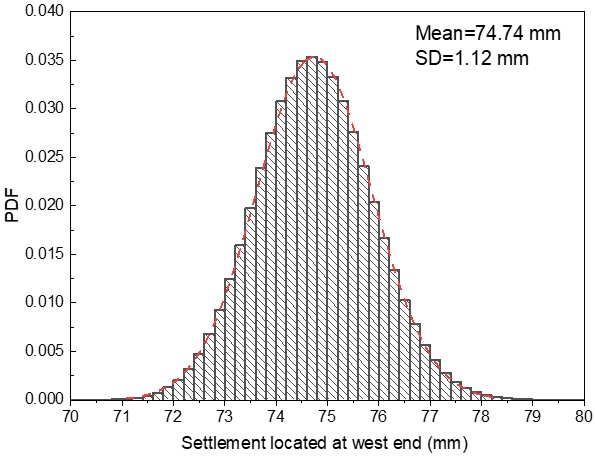
Bayesian probability theory in geotechnical engineering
The Bayesian probabilistic theory has been applied in numerous geotechnical problems to perform model selection, parameters update and uncertainty quantification, aiming to improve the prediction accuracy and provide the basis for a reliability analysis. For example, selecting the most plausible/suitable creep model of soft soil using laboratory measurements, updating the soil parameters using observed wall deflection of braced excavations, etc.
Experimental and model study of shield tunneling
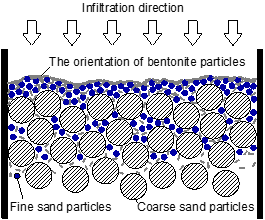
Pressure infiltration characteristics of bentonite slurry and foam for shield tunneling
We use a modified setup involving microscopic analysis and photography to gain a quantitative understanding of their sealing behavior in trenchless tunneling technologies. The properties and capabilities of modified drilling fluids have been tested when facing highly permeable stratum.
Member: Qin Su, Huang He
Related Publication: Paper1,
Modelling and stability assessment of exaction zone
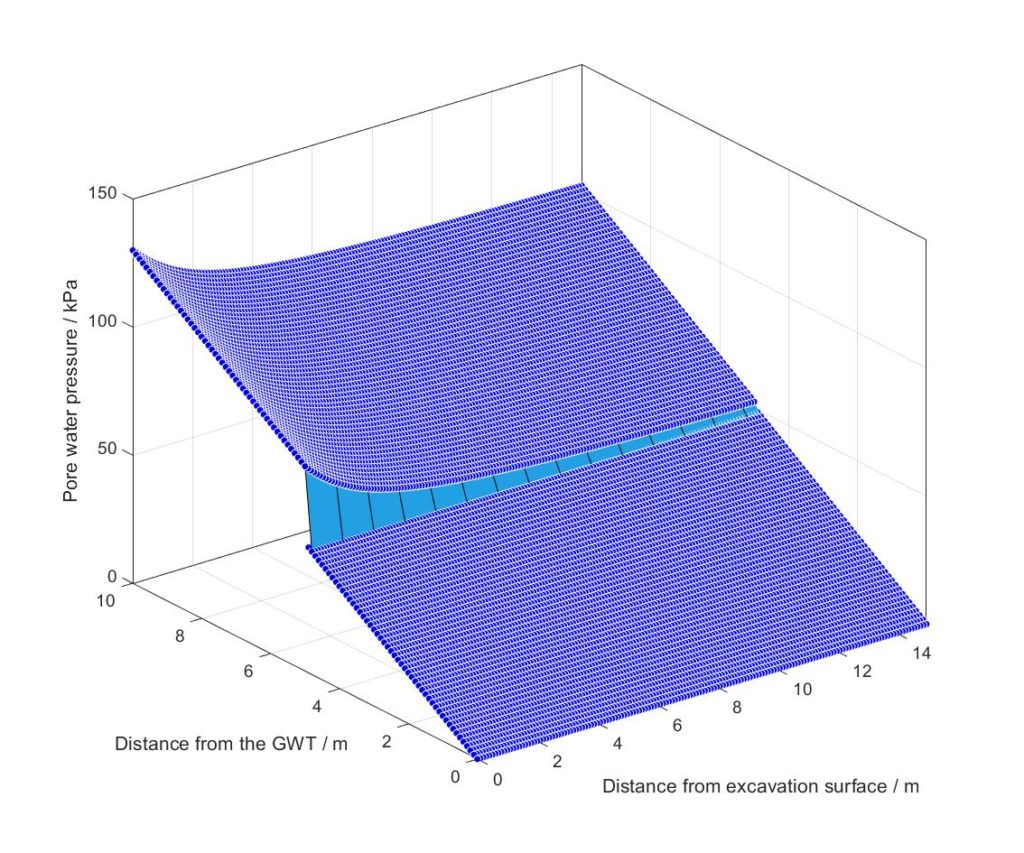
The stability of the excavation zone is one of the focuses of this topic. Based on the limit analysis theory, an analytical scheme describes the pore pressure distribution and combined the upper bound analysis is proposed to evaluate its stability.
Member: Cheng Yang
Geological Uncertainty
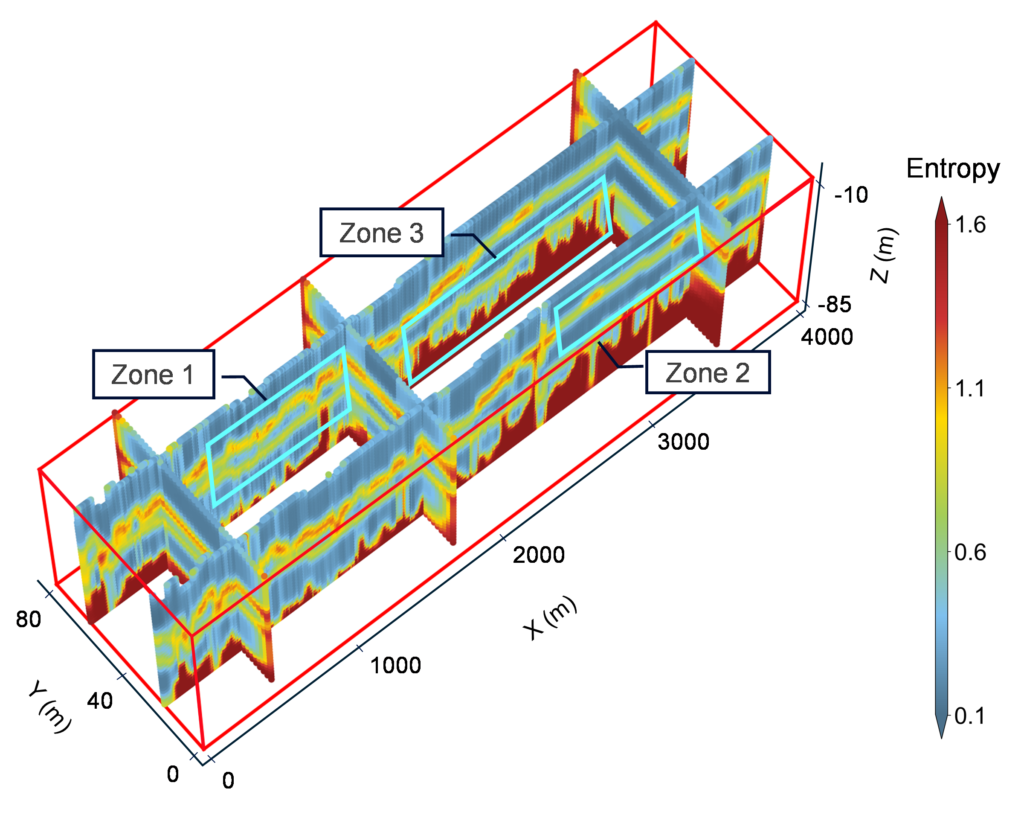
Uncertainty stratigraphic modelling in 3D geological model
The research focuses on the explanation of 3D geological stratigraphy with borehole data. we propose a physics-based framework with the concept of random field to measure the stratigraphic uncertainty with information entropy considering site-specific borehole information. The Scale of Fluctuation (SoF) are calibrated to the stratum thickness, to ensure the accuracy of probability distribution given by the Gaussian autocorrelation function. The entropy model is verified to improve its adaptability in practical projects in both 2D and 3D scenarios.
Member: Yan Wei
Sensing System
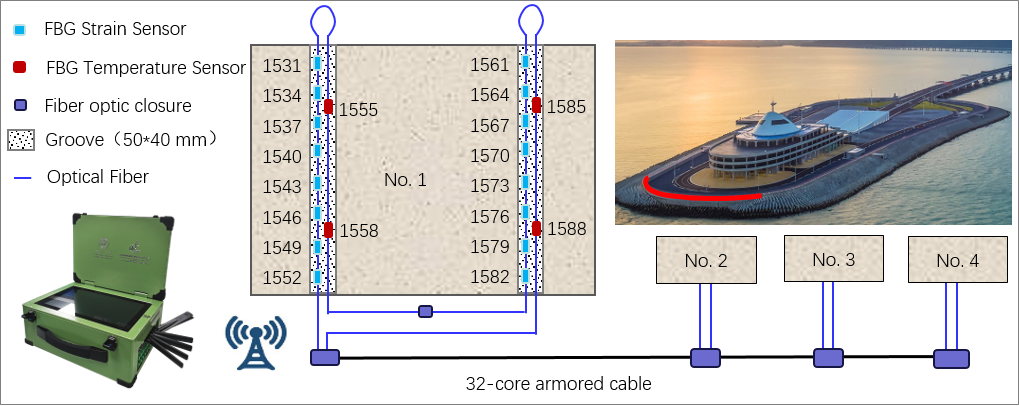
FBG-based sensing system for SHM
Fiber optic sensing technology is well suited for the structural health monitoring (SHM) of civil engineering structures. Our group has committed to develop FBG sensing systems for real-time monitoring of civil infrastructures by combining distributed temperature sensors, strain sensors, multi-dimensional displacement sensors and fiber demodulators. The proposed sensing system has been successfully applied to a subsea tunnel for its long-term structural health monitoring.
Intelligent Prediction
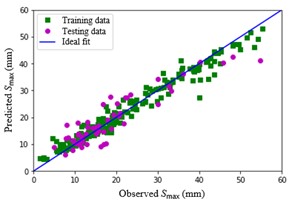
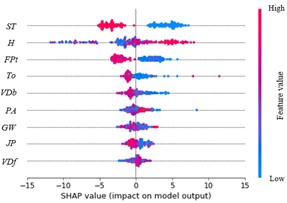
Intelligent Prediction of Tunneling-Induced Settlement Using Interpretable Models
With the limited land space, underground metro tunnel projects have been widely implemented to ease the ever-growing traffic demands in urban areas. The surface settlement, which is inevitable during tunneling, can threaten existing buildings and structures. Due to many influential factors, analysis of tunneling-induced settlement is a cumbersome task using empirical, analytical, or numerical methods. We aim to build accurate and interpretable models to predict tunneling-induced settlement based on advanced machine learning (ML) techniques.